1. Introduction:An emerging market currency is the money of a country that is in the process of economic advancement. National economies that are considered to be emerging markets typically experience an extended period of robust growth in the industrial production sector in addition to the expansion of their economy as a whole. This growth in output acts as a catalyst towards the development of infrastructure and technology.
2. The Main Countries:Although a concrete definition of an emerging market remains largely debatable, five nations are widely considered world leaders in the category. Known by the acronym BRIC they are as follows: Brazil, Russia, India, China .
Each country of BRIC has experienced explosive growth in its (GDP) along with periods of uncertainty created by debt concerns and political unrest.
As of year-end 2015, the countries of BRICS have the following global rank in GDP PPP:
* Brazil: 7th (US$3.1 trillion)
* Russia: 6th (US$3.5 trillion)
* India: 3rd (US$7.9 trillion)
* China: 1st (US$19.5 trillion)
3. Trading Emerging Market Currencies:Emerging market currencies often appear attractive to traders and investors because they typically exhibit increased volatility and dramatic exchange rate fluctuation.
Developing nations are particularly susceptible to the following factors altering perception towards their economic strength and the value of their national currency:
* Political unrest: From elections to revolutions, these create uncertainty in the areas of free markets and trade.
* Global debt markets: A tightening in the global debt market decreases the availability of working capital to developing economies. Without adequate financial input, economic growth in these regions is likely to slow.
* Monetary policy: Changes in the monetary policy of developed countries can cause a ripple effect in the foreign currency markets. For instance, if the interest rate on a major global currency is raised, emerging market currencies are likely to experience increased short-term volatility.
* Commodity pricing: A downturn in the pricing of commodities such as crude oil, natural gas, foodstuffs and precious metals may serve as a precursor to a widespread stagnation of economic growth.
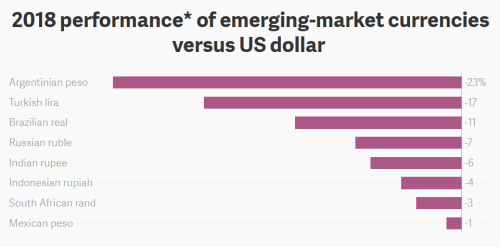
4. The Important Factors in the 4 economies :
a. BRAZILIAN REAL (BRL):
Brazil’s rise to global economic prominence is largely due to a strong exports sector. Earning a global rank of 25th, and valued at US$190.1 billion annually, the country relies heavily upon key exports of iron ore, soybeans, coffee and automobiles. Its leading trade partners are China, the United States and Argentina. From 2013 to 2016, Brazil boasted a 22.3% growth in GDP gaining a place among the world’s fastest growing economies.
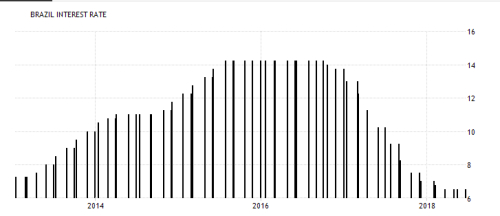
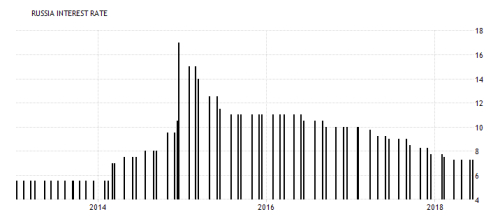
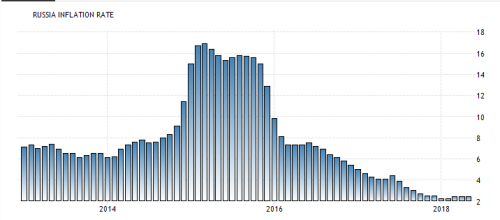
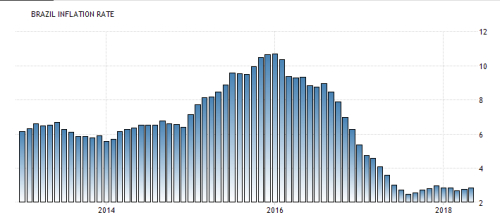 b- RUSSIAN RUBLE (RUB) :
b- RUSSIAN RUBLE (RUB) :Russia has undergone an economic metamorphosis since collapse of the Soviet Union. Free-market principles now take the place of a government-planned economy, with prosperity and industrial output becoming more prevalent. Russia is the 15th largest international exporter, eclipsing US$341 billion annually . Russia relies heavily upon the export of petroleum products and natural gas to trade partners in the European Union (EU), China and Japan. For the period of 2013 to 2016, Russian GDP grew 26.6%, enabling the country to become one of the world’s key emerging markets.
 C. INDIAN RUPEE (INR)
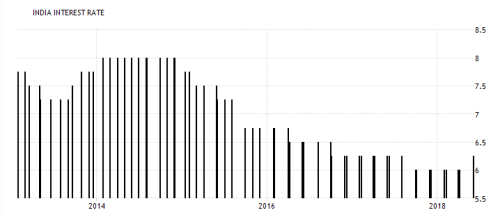
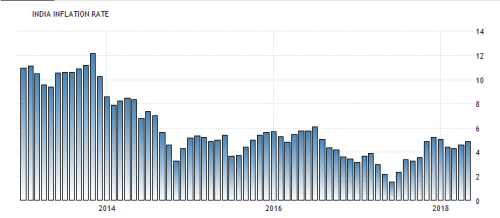
C. INDIAN RUPEE (INR) The rupee is tied with the Russian ruble , India operates as a service-based economy. Services account for 45% of India’s GDP, and jobs related to the service sector account for 31% of the workforce. Other important parts of India’s economy are the agricultural sector and the exportation of petroleum products. India’s largest trading partners are the United States, United Arab Emirates, Hong Kong and Saudi Arabia.
 D. CHINESE YUAN (CNY):
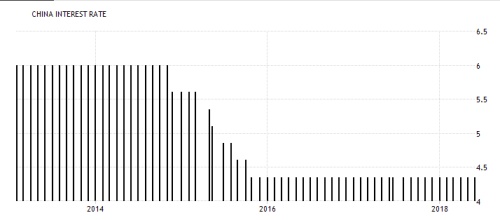
D. CHINESE YUAN (CNY):The Chinese yuan is the eighth most frequently traded currency in the world . The yuan is a rare emerging market currency in that it plays a substantial role in the foreign exchange market as a whole. Easily the currency leader of the BRIC nations, traded volumes of the CNY approaches levels of the (CHF), and is not far behind the other seven major global currencies.
The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) permits the yuan to trade openly within a moving range of 2%, which is based upon the value of the currency against a weighted basket of international currencies. The US dollar accounts for a 25% share of the weighted basket
 5.Conclusion:
5.Conclusion:Active trading of emerging market currencies on the forex offers individuals the ability to profit from increased volatility and uncertainty facing developing countries. However, risk in such markets can be great, and numerous external factors can contribute to wild swings in exchange rate pricing. The value of commodities, political change, debt concerns and international monetary policy must be taken into account before engaging these products .